Episode 6: Germany ... triumphant?
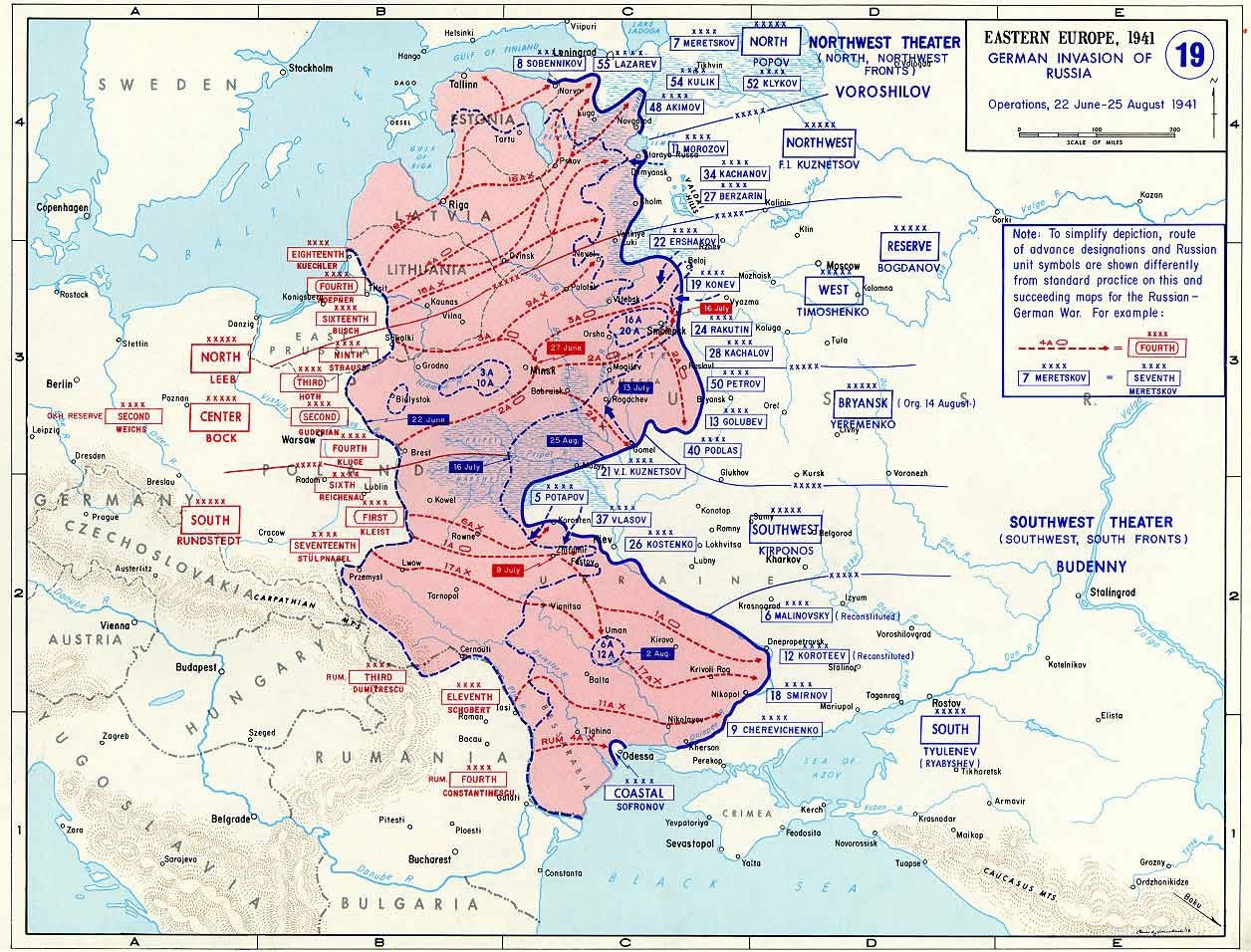
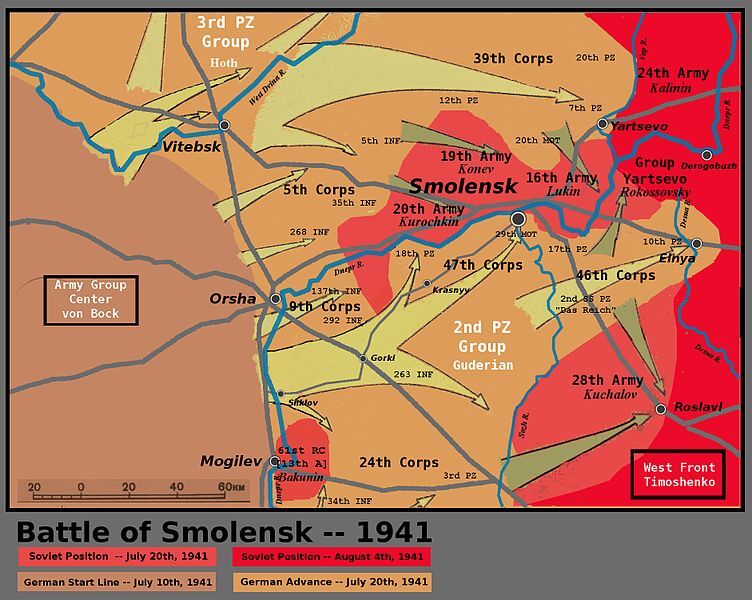
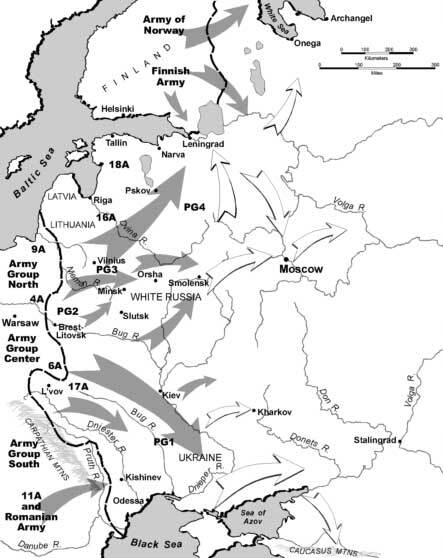
We focus on the progress of German Army Group Centre to Smolensk in July 1941.
This episode sponsored by The Eastern Front Trilogy, the true story of a Canadian drafted into the Red Army in World War II.
All proceeds from the sales of The Eastern Front Trilogy in paperback or its constituent e-books will go to helping Ukrainian refugees until all Ukrainians can return home safe from Russian military aggression.
Contact the author by email to contact@writtenword.ca
Support the podcast on Patreon.
Books cited in this episode:
David Glantz: Operation Barbarossa: Hitler's Invasion of Russia 1941. Stroud, Gloucetershire, UK, 2011.
David Stahel: Operation Barbarossa and Germany's Defeat in the East. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2009.